Abstract
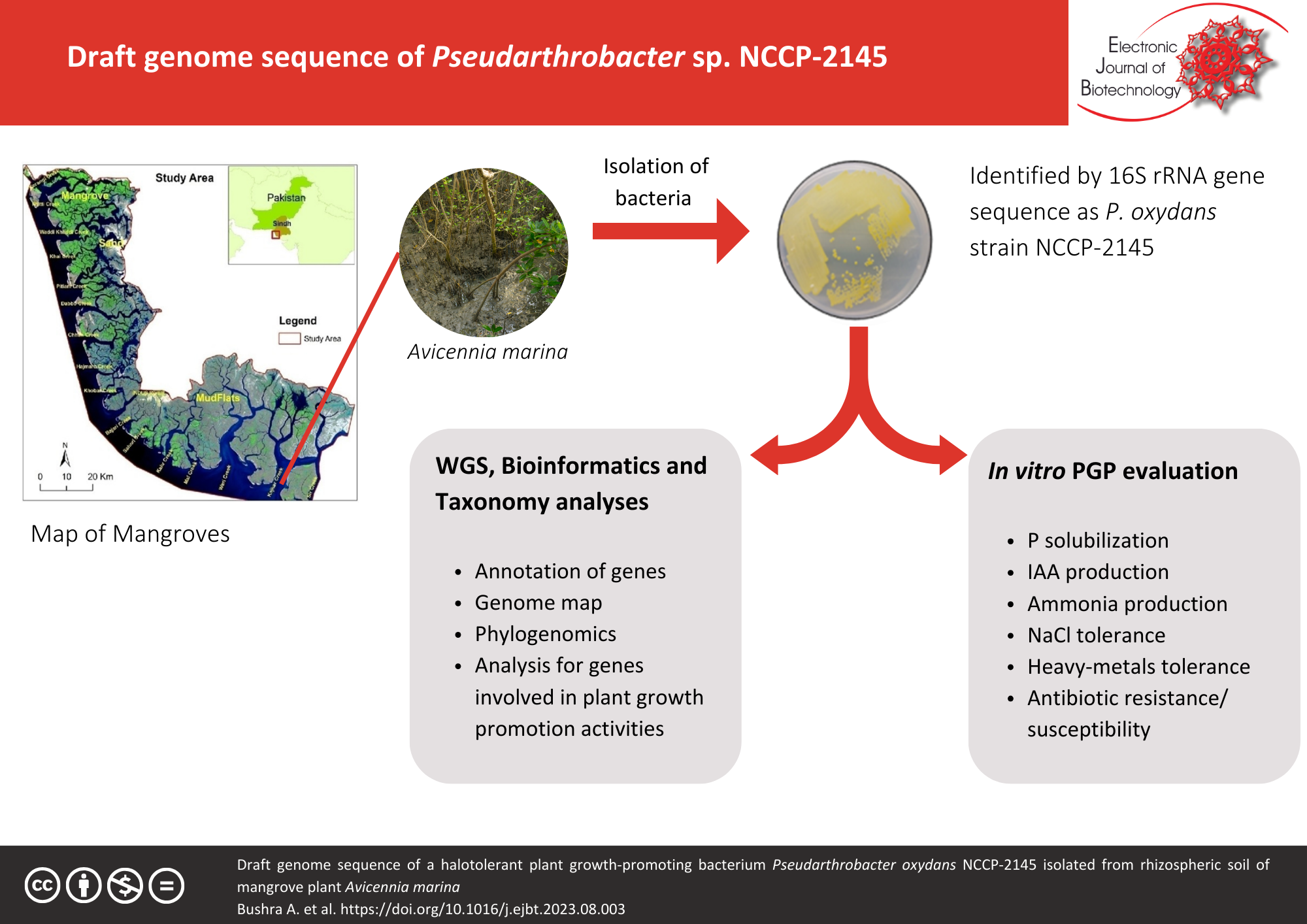
Background: Limited knowledge exists regarding the diversity of mangrove plant-associated Pseudarthrobacter species. This study presents the first draft genome and phylogenetic analysis of a Pseudarthrobacter oxydans NCCP-2145, isolated from the rhizospheric soil of Aviciana marina, a native mangrove plant found in Miani Hor, Lasbela-Baluchistan, Pakistan.
Results: The genome of P. oxydans NCCP-2145 comprises 4,495,869 base pairs, with a G+C content of 65.9% and 4,207 coding sequences. Genome annotation revealed the presence of multiple biosynthesis pathways. The analysis also identified genes responsible for plant growth-promoting traits, such as the synthesis of indole acetic acid, nitrogen fixation, and phosphorus solubilization. Experimental evaluations confirmed strain NCCP-2145 positive reactions for phosphorus solubilization, indole-3-acetic acid production, and ammonia production. Furthermore, strain NCCP-2145 exhibited tolerance to heavy metals (nickel, copper, and cadmium) and salinity levels up to 10% NaCl. Antibiotic susceptibility testing indicated resistance only to ceftazidime and the combination of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid. For phylogenomic analysis, strain NCCP-2145 was analyzed and compared to the closely related validly published type species P. oxydans DSM 20119T, revealing a similarity score of 98.64% based on 16S rRNA gene sequences and 89.1% based on DNA-DNA hybridization, confirming its classification as a member of species, P. oxydans.
Conclusions: This study significantly contributes to our understanding of the genomic characteristics, functional capabilities, and potential plant growth-promoting attributes of P. oxydans NCCP-2145. Future research should focus on unraveling the precise mechanisms underlying its plant growth-promoting abilities and exploring practical applications in sustainable agriculture and environmental restoration.
References
Tshishonga K, Serepa-Dlamini MH. Draft genome sequence of Pseudarthrobacter phenanthrenivorans Strain MHSD1, a bacterial endophyte isolated from the medicinal plant Pellaea calomelanos. Evol Bioinform Online. 2020;16:1176934320913257. https://doi.org/10.1177/1176934320913257 PMid: 32284671
Ham SH, Yoon AR, Oh HE, et al. Plant growth-promoting microorganism Pseudarthrobacter sp. NIBRBAC000502770 enhances the growth and flavonoid content of Geum aleppicum. Microorganisms. 2022;10(6):1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061241 PMid: 35744759
Amaresan N, Kumar MS, Annapurna K, Kumar K, Sankaranaryanan N. Beneficial microbes in agro-ecology: Bacteria and fungi. United Kingdom: Academic Press; 2020. 936 p. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2020-0-00594-3
Jiang Y, Song Y, Jiang C, et al. Identification and characterization of Arthrobacter nicotinovorans JI39, a novel plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria strain from Panax ginseng. Frontiers in Plant Science. 2022;13:873621. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.873621 PMid: 35615118
Issifu M, Songoro EK, Onguso J, et al. Potential of Pseudarthrobacter chlorophenolicus BF2P4-5 as a biofertilizer for the growth promotion of tomato plants. Bacteria. 2022;1(4):191-206. https://doi.org/10.3390/bacteria1040015
Carter MR, Gregorich EG. Soil sampling and methods of analysis. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2007. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420005271
Pikovskaya R. Mobilization of phosphorus in soil in connection with vital activity of some microbial species. Mikrobiologiya. 1948;17:362-370.
Demissie S, Muleta D, Berecha G. Effect of phosphate solubilizing bacteria on seed germination and seedling growth of faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Int J Agric Res. 2013;8(3):123-136. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijar.2013.123.136
Kumari S, Prabha C, Singh A, et al. Optimization of indole-3-acetic acid production by diazotrophic B. subtilis DR2 (KP455653), isolated from rhizosphere of Eragrostis cynosuroides. Int J Pharma Med Biol Sci. 2018;7(2):20-27. https://doi.org/10.18178/ijpmbs.7.2.20-27
Forhad MH, Khaledur Rahman SM, Shahedur Rahman M, et al. Probiotic properties analysis of isolated lactic acid bacteria from buffalo milk. Arch Clin Microbiol. 2015;7(1):5-10.
Agbodjato NA, Noumavo PA, Baba-Moussa F, et al. Characterization of potential plant growth promoting rhizobacteria isolated from Maize (Zea mays L.) in central and Northern Benin (West Africa). Appl Environ Soil Sci. 2015;2015:901656. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/901656
Ali A, Liaqat S, Tariq H, et al. Neonatal calf diarrhea: A potent reservoir of multi-drug resistant bacteria, environmental contamination and public health hazard in Pakistan. Sci Total Environ. 2021;799:149450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149450 PMid: 34426357.
Carrasco-Fernández J, Guerra M, Castro JF, et al. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria from Juan Fernández archipelago improve germination rate of endangered plant Solanum fernandezianum Phil. Chilean J Agr Res. 2020;80(1):41-49. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-58392020000100041
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(15):2114-2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170 PMid: 24695404
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, et al. SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol. 2012;19(5):455-477. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2012.0021 PMid: 22506599
Parks DH, Imelfort M, Skennerton CT, et al. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Gen Res. 2015;25(7):1043-1055. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.186072.114 PMid: 25977477
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, et al. Introducing EzBioCloud: A taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2017;67(5):1613-1617 https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001755 PMid: 28005526
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Göker M. TYGS is an automated high-throughput platform for state-of-the-art genome-based taxonomy. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):2182. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10210-3 PMid: 31097708
Busse HJ. Review of the taxonomy of the genus Arthrobacter, emendation of the genus Arthrobacter sensu lato, proposal to reclassify selected species of the genus Arthrobacter in the novel genera Glutamicibacter gen. nov., Paeniglutamicibacter gen. nov., Pseudoglutamicibacter gen. nov., Paenarthrobacter gen. nov. and Pseudarthrobacter gen. nov., and emended description of Arthrobacter roseus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2016;66(1):9-37. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000702 PMid: 26486726
Wu Y-p, Liu D-m, Zhao S, et al. Assessing the safety and probiotic characteristics of Bacillus coagulans 13002 based on complete genome and phenotype analysis. LWT. 2022;155:112847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112847
Kumar V, Singh S, Singh J, et al. Potential of plant growth promoting traits by bacteria isolated from heavy metal contaminated soils. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 2015;94(6):807-814. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1523-7 PMid: 25782590
Minaxi, Nain L, Yadav R, et al. Characterization of multifaceted Bacillus sp. RM-2 for its use as plant growth promoting bioinoculant for crops grown in semi arid deserts. Appl Soil Ecol. 2012;59:124-135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2011.08.001
Shiva Shanker A, Reddy DM, Padmavati K, Pindi PK. Potential bio-control agent Serratia sp. SCP Isolated from rhizosphere soil, Mahbubnagar, Telangana. Open Acc J Bio Sci. 2022; 4(4):1913-1922.
Wash P, Batool A, Mulk S, et al. Prevalence of antimicrobial resistance and respective genes among Bacillus spp., a versatile bio-fungicide. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(22):14997. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192214997 PMid: 36429716
Mahdi I, Fahsi N, Hijri M, Sobeh M. Antibiotic resistance in plant growth promoting bacteria: A comprehensive review and future perspectives to mitigate potential gene invasion risks. Front Microbiol. 2022;13:999988. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.999988 PMid: 36204627
Gupta R, Kumari A, Sharma S, et al. Identification, characterization and optimization of phosphate solubilizing rhizobacteria (PSRB) from rice rhizosphere. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022;29(1):35-42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.075 PMid: 35002393
Bhat MA, Kumar V, Bhat MA, et al. Mechanistic Insights of the interaction of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) with plant roots toward enhancing plant productivity by alleviating salinity stress. Front Microbiol. 2020;11:1952. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.01952 PMid: 32973708
Gebicka L, Krych-Madej J. The role of catalases in the prevention/promotion of oxidative stress. J Inorg Biochem. 2019;197:110699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2019.110699 PMid: 31055214
Pranita M, Petkar M. Isolation, screening and identification of indole acetic acid (IAA) producing bacteria from rhizospheric soil. Int J Sci Res. 2018;7(3):1725-1731.
Kalayu G. Phosphate solubilizing microorganisms: Promising approach as biofertilizers. Int J Agron. 2019;2019:4917256. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4917256
Mechirackal Balan B, Shini S, Krishnan KP, et al. Mercury tolerance and biosorption in bacteria isolated from Ny-Ålesund, Svalbard, Arctic. J Basic Microbiol. 2018;58(4):286-295. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201700496 PMid: 29384200
Oubohssaine M, Sbabou L, Aurag J. Native heavy metal-tolerant plant growth promoting rhizobacteria improves Sulla spinosissima (L.) growth in post-mining Contaminated Soils. Microorganisms. 2022;10(5):838. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10050838 PMid: 35630284
Sajid M, Khan M, Rab A, et al. Impact of nitrogen and phosphorus on seed yield and yield components of Okra cultivars. J Anim Plant Sci. 2012;22(3):704-707.
McGrath JW, Chin JP, Quinn JP. Organophosphonates revealed: New insights into the microbial metabolism of ancient molecules. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 2013;11(6):412-419. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3011 PMid: 23624813
Lesmeister KE, Heinrichs AJ, Gabler MT. Effects of supplemental yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) culture on rumen development, growth characteristics, and blood parameters in neonatal dairy calves. Journal of Dairy Science. 2004;87(6):1832-1839. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(04)73340-8 PMid: 15453499
Duca DR, Rose DR, Glick BR. Indole acetic acid overproduction transformants of the rhizobacterium Pseudomonas sp. UW4. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. 2018;111:1645-1660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-018-1051-7 PMid: 29492769
Spaepen S, Das F, Luyten E, et al. Indole-3-acetic acid-regulated genes in Rhizobium etli CNPAF512. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2009;291(2):195-200. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01453.x PMid: 19087205
Franche C, Lindström K, Elmerich C. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria associated with leguminous and non-leguminous plants. Plant Soil 2009;321:35-59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9833-8
Gaby JC, Buckley DH. Assessment of nitrogenase diversity in the environment. In: de Bruijn FJ, editor. Biological Nitrogen Fixation. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2015. p. 209-216.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) 2023 Electronic Journal of Biotechnology