Abstract
Background: It has been reported that circular RNA formin 2 (circFMN2) can motivate colorectal cancer (CRC) proliferation. However, the effect of circFMN2 on the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in the CRC tumor microenvironment remains unclear. The study was to figure out the latent mechanism by which circFMN2 impacts TAM polarization to motivate the malignant behavior of CRC cells.
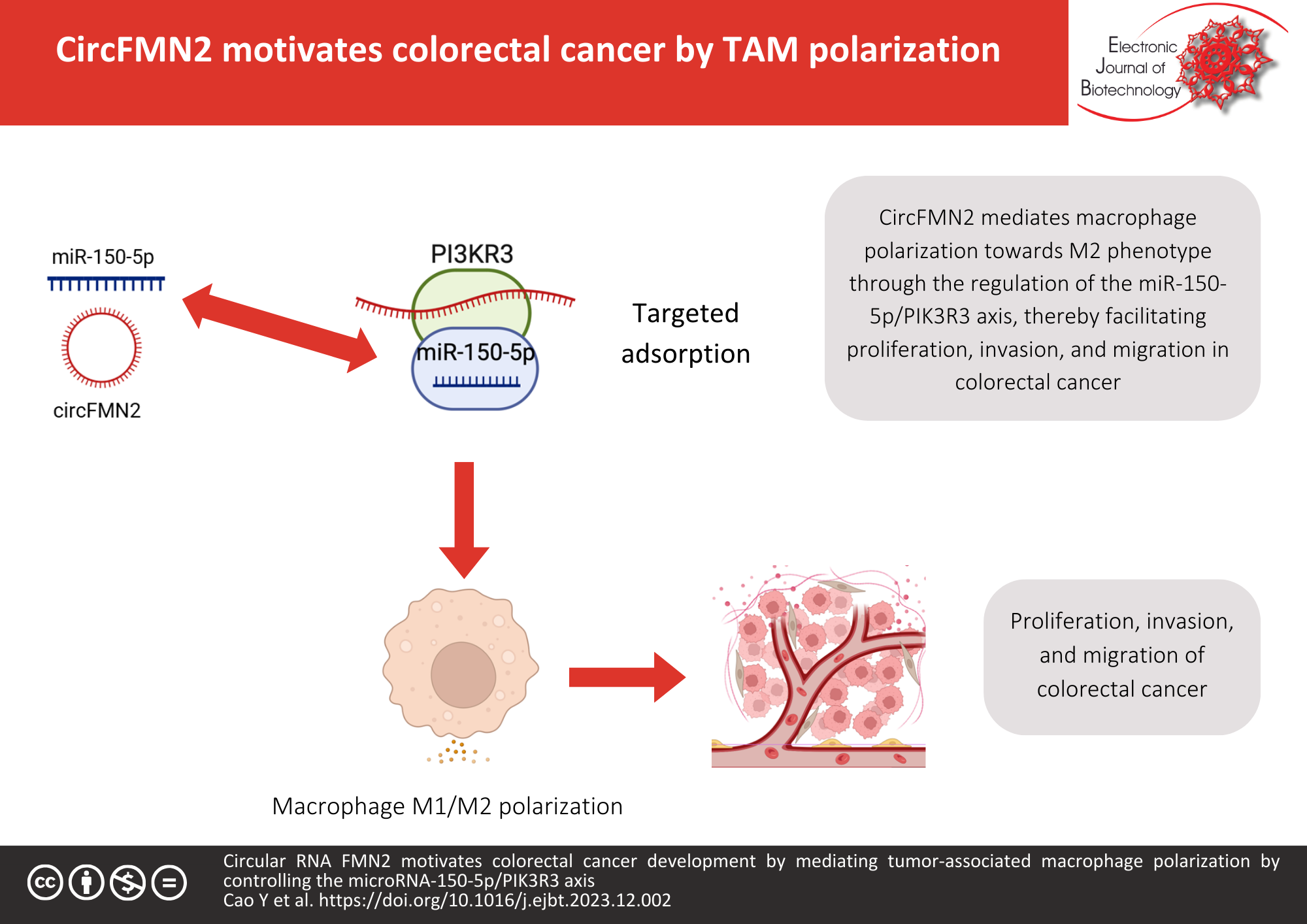
Results: circFMN2 and PIK3R3 levels were reduced in M1 macrophages but elevated in M2 macrophages, whereas miR-150-5p level was the opposite. circFMN2 knockdown downregulated M2 macrophage markers CD163, CCL22 and CD206 and upregulated M1 macrophage markers CD86, TNF-α and IL-1β in M2 macrophages. Co-culture with M2 macrophage-conditioned medium with circFMN2 knockdown reduced CRC proliferation, invasion, and migration, while knockdown of miR-150-5p had the opposite effect. CircFMN2 adsorbed miR-150-5p to mediate PIK3R3 in M2 macrophages. Overexpression of miR-150-5p can reverse the promoting effects of overexpression of circFMN2 on M2 polarization, CRC cell proliferation, invasion, and migration. Elevation of PIK3R3 could turn around the repressive effect of circFMN2 knockdown on M2 polarization and CRC cell proliferation, invasion, and migration. In an in vivo model, M2 macrophages expressing low or high circFMN2 were co-transplanted with CRC cells into nude mice, resulting in inhibition and promotion of tumor growth, respectively.
Conclusions: All in all, circFMN2 mediates TAM polarization to M2 type by controlling the miR-150-5p/PIK3R3 axis to motivate CRC development and may offer a latent molecular target for CRC treatment.
References
Siegel R, Miller K, Fuchs H, et al. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA: A cancer journal for clinicians 2021;71(1):7-33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21654 PMid: 33433946
Bien J, Lin A. A review of the diagnosis and treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. JAMA 2021;325(23):2404-2405. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.6021 PMid: 34129003
Cardoso R, Guo F, Heisser T, et al. Colorectal cancer incidence, mortality, and stage distribution in European countries in the colorectal cancer screening era: an international population-based study. The Lancet Oncology 2021;22(7):1002-1013. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00199-6 PMid: 34048685
Ma W, Wang K, Nguyen L, et al. Association of screening lower endoscopy with colorectal cancer incidence and mortality in adults older than 75 years. JAMA oncology 2021;7(7):985-992. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.1364 PMid: 34014275
Tsilimigras D, Brodt P, Clavien P, et al. Liver metastases. Nature reviews Disease primers 2021;7(1):27. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-021-00261-6 PMid: 33859205
Wang S, Pang L, Liu Z, et al. SERPINE1 associated with remodeling of the tumor microenvironment in colon cancer progression: a novel therapeutic target. BMC cancer 2021;21(1):767. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-021-08536-7 PMid: 34215248
Nenkov M, Ma Y, Gaßler N, et al. Metabolic reprogramming of colorectal cancer cells and the microenvironment: implication for therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021;22(12):6262. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126262 PMid: 34200820
Eisinger S, Sarhan D, Boura V, et al. Targeting a scavenger receptor on tumor-associated macrophages activates tumor cell killing by natural killer cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2020;117(50):32005-32016. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2015343117 PMid: 33229588
Min A, Mimura K, Nakajima S, et al. Therapeutic potential of anti-VEGF receptor 2 therapy targeting for M2-tumor-associated macrophages in colorectal cancer. Cancer immunology, Immunotherapy, 2021;70(2):289-298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-020-02676-8 PMid: 32705303
Pan Y, Yu Y, Wang X, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages in tumor immunity. Frontiers in Immunology 2020;11:583084. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.583084 PMid: 33365025
Di Martile M, Farini V, Consonni F, et al. Melanoma-specific bcl-2 promotes a protumoral M2-like phenotype by tumor-associated macrophages. Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer 2020;8(1):e000489. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2019-000489 PMid: 32269145
Li C, Xue V, Wang Q, et al. The Mincle/Syk/NF-?B signaling circuit is essential for maintaining the protumoral activities of tumor-associated macrophages. Cancer Immunology Research 2020;8(8):1004-1017. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-19-0782 PMid: 32532809
Lu Q, Wang X, Zhu J, et al. Hypoxic tumor-derived exosomal Circ0048117 facilitates M2 macrophage polarization acting as miR-140 sponge in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. OncoTargets and Therapy 2020;13:11883-11897. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S284192 PMid: 33239890
Wang X, Sheng W, Xu T, et al. CircRNA hsa_circ_0110102 inhibited macrophage activation and hepatocellular carcinoma progression via miR-580-5p/PPAR?/CCL2 pathway. Aging. 2021;13(8):11969-11987. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.202900 PMid: 33891564
Hu Z, Zhou S, Li J, et al. Circular RNA sequencing identifies CircASAP1 as a key regulator in hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. Hepatology 2020;72(3):906-922.
Li Y, Li C, Xu R, et al. A novel circFMN2 promotes tumor proliferation in CRC by regulating the miR-1182/hTERT signaling pathways. Clinical Science 2019;133(24):2463-2479.
Lou T, Ke K, Zhang L, et al. LncRNA PART1 facilitates the malignant progression of colorectal cancer via miR-150-5p/LRG1 axis. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 2020;121(10):4271-4281.
Xu H, Liu Y, Cheng P, et al. CircRNA_0000392 promotes colorectal cancer progression through the miR-193a-5p/PIK3R3/AKT axis. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 2020;39(1):283.
Zhang J, Zhang Y, Li X, Wang H, et al. MicroRNA?212 inhibits colorectal cancer cell viability and invasion by directly targeting PIK3R3. Molecular Medicine Reports. 2017;16(5):7864-7872. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.7552. (Retraction published Molecular Medicine Reports 2023;28(1):138).
Shan G, Shao B, Liu Q, et al. circFMN2 sponges miR-1238 to promote the expression of LIM-homeobox gene 2 in prostate cancer cells. Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids. 2020;21:133-146.
Tang S, Ning Q, Yang L, et al. Mechanisms of immune escape in the cancer immune cycle. International Immunopharmacology 2020;86:106700.
Wang X, Yao Y, Jin M. Circ-0001068 is a novel biomarker for ovarian cancer and inducer of PD1 expression in T cells. Aging 2020;12(19):19095-19106.
Sun H, Feng X. MicroRNA-367 directly targets PIK3R3 to inhibit proliferation and invasion of oral carcinoma cells. Bioscience Reports 2020;40(5):BSR20193867. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20193867 (Retraction published Bioscience Reports 2022;42(11):BSR-2019-3867_RET).
Xu W, Yu M, Qin J, et al. LACTB Regulates PIK3R3 to promote autophagy and inhibit EMT and proliferation through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in colorectal cancer. Cancer Management and Research. 2020;12:5181-5200.
Sun Q, Yang Z, Li P, et al. A novel miRNA identified in GRSF1 complex drives the metastasis via the PIK3R3/AKT/NF-?B and TIMP3/MMP9 pathways in cervical cancer cells. Cell Death & Disease 2019;10(9):636.
Ibrahim S, Li G, Hu F, et al. PIK3R3 promotes chemotherapeutic sensitivity of colorectal cancer through PIK3R3/NF-kB/TP pathway. Cancer Biology & Therapy 2018;19(3):222-229.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) 2024 Electronic Journal of Biotechnology