Abstract
Background: At present, research on facile, green synthesis of nanoparticles has significantly increased because of its fast, one-step, cost-effective, time-efficient, and non-toxic nature. In this study, we have reported a single-step green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using cell wall polysaccharides of a hot spring origin, thermotolerant Bacillus species.
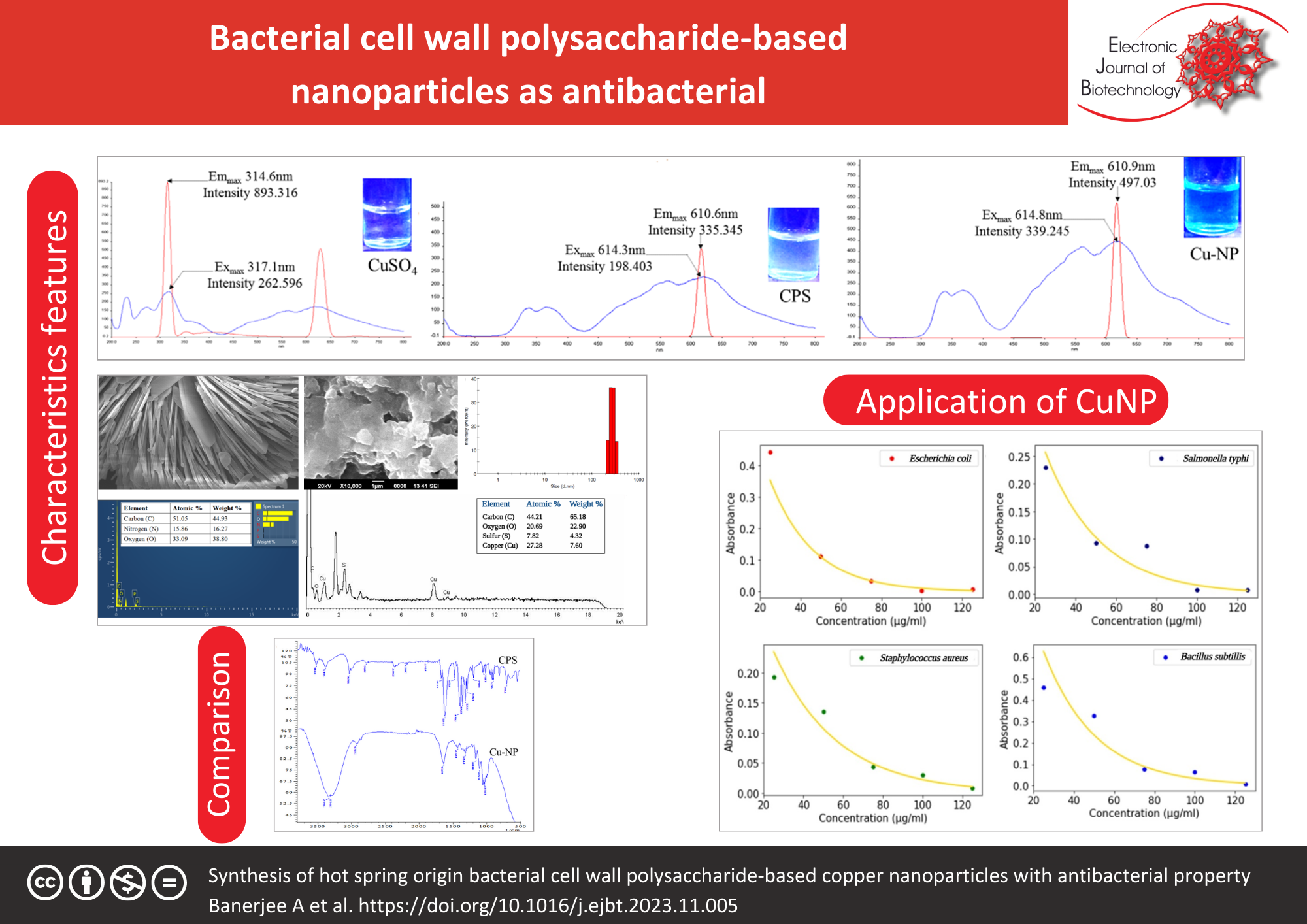
Result: Copper nanoparticles were characterized using UV-visible spectrophotometry, fluorescence and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy with energy dispersive spectroscopy, particle size, and zeta potential analyses. UV-visible spectra of synthesized copper nanoparticles exhibited a band cantered between 220–235 nm, characteristic spectra of copper oxide nanoparticles. Infrared spectra showed the band at 490-530 cm−1 corresponding to metal-oxygen or copper nanoparticle vibration, supporting the presence of copper oxide nanoparticles in the monoclinic phase. The energy dispersive spectra of copper nanoparticles exhibited a strong signal from elemental copper. The dynamic Light Scattering pattern confirmed the nanoparticle nature of the studied sample. These nanoparticles showed preferential activity against gram-negative pathogens, Salmonella typhi and Escherichia coli. The thermodynamic nature of the nanoparticles is also established for its antibacterial actions.
Conclusions: The antibacterial action and its thermodynamics reinforce the possible use of copper nanoparticles as an alternative to commercially available antimicrobials. This study may open a new path for future studies to treat harmful microorganisms resistant to traditional antibiotics in a greener way.
References
Banerjee A, Halder U, Bandopadhyay R. Preparations and applications of polysaccharide based green synthesized metal nanoparticles: a state-of-the-art. Journal of Cluster Science 2017;28:1803-1813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-017-1219-8
Sathiyanarayanan G, Dineshkumar K, Yang YH. Microbial exopolysaccharide-mediated synthesis and stabilization of metal nanoparticles. Critical Reviews in Microbiology 2017;43(6):731-752. https://doi.org/10.1080/1040841X.2017.1306689 PMid: 28440091
Liu J, Qin G, Raveendran P, et al. Facile “green” synthesis, characterization, and catalytic function of ??D?glucose?stabilized Au nanocrystals. Chemistry–A European Journal 2006;12(8):2131-2138. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.200500925 PMid: 16358347
Balantrapu K, Goia DV. Silver nanoparticles for printable electronics and biological applications. Journal of Materials Research 2009;24(9):2828-2836. https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0336
Vollmer W, Bertsche U. Murein (peptidoglycan) structure, architecture and biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes 2008;1778(9):1714-1734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.06.007 PMid: 17658458
Turner RD, Mesnage S, Hobbs JK, et al. Molecular imaging of glycan chains couples cell-wall polysaccharide architecture to bacterial cell morphology. Nature Communications 2018;9(1):1263. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03551-y PMid: 29593214
Arendsen LP, Thakar R, Sultan AH. The use of copper as an antimicrobial agent in health care, including obstetrics and gynecology. Clinical Microbiology Reviews 2019;32(4):e00125-18. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00125-18 PMid: 31413046
Chatterjee AK, Sarkar RK, Chattopadhyay AP, et al. A simple robust method for synthesis of metallic copper nanoparticles of high antibacterial potency against E. coli. Nanotechnology 2012;23(8):085103. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/23/8/085103 PMid: 22293320
Cho KH, Park JE, Osaka T, et al. The study of antimicrobial activity and preservative effects of nanosilver ingredient. Electrochimica Acta 2005;51(5):956-960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2005.04.071
Jung WK, Koo HC, Kim KW, et al. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of the silver ion in Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2008;74(7):2171-2178. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02001-07 PMid: 18245232
Durán N, Marcato PD, De Souza GI, et al. Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles produced by fungal process on textile fabrics and their effluent treatment. Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology 2007;3(2):203-208. https://doi.org/10.1166/jbn.2007.022
Manjari G, Saran S, Arun T, et al. Facile Aglaia elaeagnoidea mediated synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles: antioxidant and catalysis properties. Journal of Cluster Science 2017;28:2041-2056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-017-1199-8
Sarkar S, Ponce NT, Banerjee A, et al. Green polymeric nanomaterials for the photocatalytic degradation of dyes: a review. Environmental Chemistry Letters 2020;18:1569-1580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01021-w PMid: 32837482
Rajoka MSR, Mehwish HM, Zhang H, et al. Antibacterial and antioxidant activity of exopolysaccharide mediated silver nanoparticle synthesized by Lactobacillus brevis isolated from Chinese koumiss. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2020;186:110734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110734 PMid: 31865119
Ruparelia JP, Chatterjee AK, Duttagupta SP, et al. Strain specificity in antimicrobial activity of silver and copper nanoparticles. Acta Biomaterialia 2008;4(3):707-716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2007.11.006 PMid: 18248860
Gopalakrishnan V, Muniraj S. Neem flower extract assisted green synthesis of copper nanoparticles–optimisation, characterisation and anti-bacterial study. Materials Today: Proceedings 2021;36:832-836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.07.013
Wang L, Hu C, Shao L. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: present situation and prospects for the future. International Journal of Nanomedicine 2017;12:1227. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S121956 PMid: 28243086
Usha R, Prabu E, Palaniswamy M, et al. Synthesis of metal oxide nano particles by Streptomyces sp. for development of antimicrobial textiles. Global Journal of Biotechnology & Biochemistry 2010;5(3):153-160.
Singh AV, Patil R, Anand A, et al. Biological synthesis of copper oxide nano particles using Escherichia coli. Current Nanoscience 2010;6(4):365-369. https://doi.org/10.2174/157341310791659062
Mukherjee P. Stenotrophomonas and Microbacterium: mediated biogenesis of copper, silver and iron nanoparticles—Proteomic insights and antibacterial properties versus biofilm formation. Journal of Cluster Science 2017;28:331-358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-016-1097-5
Brandão IYDNV, de Macedo EF, de Souza Silva PHB, et al. Bionanomining of copper-based nanoparticles using pre-processed mine tailings as the precursor. Journal of Environmental Management 2023;338:117804-117812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.117804 PMid: 36996570
Borkow G, Gabbay J, Dardik R, et al. Molecular mechanisms of enhanced wound healing by copper oxide?impregnated dressings. Wound Repair and Regeneration 2010;18(2):266-275. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-475X.2010.00573.x PMid: 20409151
Borkow G, Zatcoff RC, Gabbay J. Reducing the risk of skin pathologies in diabetics by using copper impregnated socks. Medical Hypotheses 2009;73(6):883-886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2009.02.050 PMid: 19559540
Banerjee A, Halder U, Chaudhry V, et al. Draft genome sequence of the nonpathogenic, thermotolerant, and exopolysaccharide-producing Bacillus anthracis strain PFAB2 from Panifala hot water spring in West Bengal, India. Genome Announcements 2016;4(6):e01346-16. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.01346-16 PMid: 28007848
Banerjee A, Rudra SG, Mazumder K, et al. Structural and functional properties of exopolysaccharide excreted by a novel Bacillus anthracis (Strain PFAB2) of hot spring origin. Indian Journal of Microbiology 2018;58:39-50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-017-0699-4 PMid: 29434396
Mandal D, Dash SK, Das B, et al. Bio-fabricated silver nanoparticles preferentially targets Gram positive depending on cell surface charge. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2016;83:548-558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.07.011 PMid: 27449536
Banerjee A, Das D, Rudra SG, et al. Characterization of exopolysaccharide produced by Pseudomonas sp. PFAB4 for synthesis of EPS-coated AgNPs with antimicrobial properties. Journal of Polymers and the Environment 2020;28:242-256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01602-z
Laiman V, Heriyanto DS, Lee Y L, et al. Zinc oxide nanoparticles promote YAP/TAZ nuclear localization in alveolar epithelial type II cells. Atmosphere 2022;13(2):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020334
Adhikari S, Lohar S, Kumari B, et al. Cu (II) complex of a new isoindole derivative: structure, catecholase like activity, antimicrobial properties and bio-molecular interactions. New Journal of Chemistry 2016;40(12):10094-10099. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NJ02193J
Nagpal UM, Bankar AV, Pawar NJ, et al. Equilibrium and kinetic studies on biosorption of heavy metals by leaf powder of paper mulberry (Broussonetia papyrifera). Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 2011;215:177-188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0468-z
Li YH, Di Z, Ding J, et al. Adsorption thermodynamic, kinetic and desorption studies of Pb2+ on carbon nanotubes. Water Research 2005;39(4):605-609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.11.004 PMid: 15707633
Nayak A, Sahoo J K, Sahoo SK, et al. Removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution using zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesised from Ocimum sanctum (Tulsi leaf): a green approach. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry 2022;102(19):7889-7910. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1842386
Ali Fil B, Korkmaz M, Özmetin G. An empirical model for adsorption thermodynamics of copper (II) from solutions onto illite clay-batch process design. Journal of the Chilean Chemical Society 2014;59(4):2686-2691. http://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-97072014000400012
Wu J, Xia A, Chen C, et al. Adsorption thermodynamics and dynamics of three typical dyes onto bio-adsorbent spent substrate of Pleurotus eryngii. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2019;16(5):679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050679 PMid: 30813535
Rehana D, Mahendiran D, Kumar RS, et al. Evaluation of antioxidant and anticancer activity of copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized using medicinally important plant extracts. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2017;89:1067-1077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.02.101 PMid: 28292015
Paszkiewicz M, Go??biewska A, Rajski ?, et al. Synthesis and characterization of monometallic (Ag, Cu) and bimetallic Ag-Cu particles for antibacterial and antifungal applications. Journal of Nanomaterials 2016;2016:2187940. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2187940
Pal P, Banerjee A, Soren K, et al. Novel biocide based on cationic derivative of psyllium: surface modification and antibacterial activity. Journal of Polymers and the Environment 2019;27(6):1178-1190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01419-w
Brown S, Meredith T, Swoboda J, et al. Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis W23 make polyribitol wall teichoic acids using different enzymatic pathways. Chemistry & Biology 2010;17(10):1101-1110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.07.017 PMid: 21035733
Sajna KV, Sukumaran RK, Gottumukkala LD, et al. Studies on structural and physical characteristics of a novel exopolysaccharide from Pseudozyma sp. NII 08165. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2013;59:84-89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.04.025 PMid: 23597707
Mokhtarzadeh A, Alibakhshi A, Hejazi M, et al. Bacterial-derived biopolymers: Advanced natural nanomaterials for drug delivery and tissue engineering. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2016;82:367-384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2016.06.013
Palza H. Antimicrobial polymers with metal nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2015;16(1):2099-2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16012099 PMid: 25607734
Jain PK, Huang X, El-Sayed IH, et al. Review of some interesting surface plasmon resonance-enhanced properties of noble metal nanoparticles and their applications to biosystems. Plasmonics 2007;2:107-118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-007-9031-1
Tiwari AD, Mishra AK, Mishra SB, et al. Stabilisation of silver and copper nanoparticles in a chemically modified chitosan matrix. Carbohydrate Polymers 2013;92(2):1402-1407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.10.008 PMid: 23399170
Hasheminya SM, Dehghannya J. Green synthesis and characterization of copper nanoparticles using Eryngium caucasicum Trautv aqueous extracts and its antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Particulate Science and Technology 2020;38(8):1019-1026. https://doi.org/10.1080/02726351.2019.1658664
Betancourt-Galindo R, Reyes-Rodriguez PY, Puente-Urbina B A, et al. Synthesis of copper nanoparticles by thermal decomposition and their antimicrobial properties. Journal of Nanomaterials 2014;2014:980545. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/980545
Kannan S, Solomon A, Krishnamoorthy G, et al. Liposome encapsulated surfactant abetted copper nanoparticles alleviates biofilm mediated virulence in pathogenic Pseudomonas aeruginosa and MRSA. Scientific Reports 2021;11(1):1102. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-79976-7
Berg JM, Romoser A, Banerjee N, et al. The relationship between pH and zeta potential of? 30 nm metal oxide nanoparticle suspensions relevant to in vitro toxicological evaluations. Nanotoxicology 2009;3:276-283. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390903276941
Patel BH, Channiwala MZ, Chaudhari SB, et al. Biosynthesis of copper nanoparticles; its characterization and efficacy against human pathogenic bacterium. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 2016;4(2):2163-2169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.03.046
Birch NP, Schiffman JD. Characterization of self-assembled polyelectrolyte complex nanoparticles formed from chitosan and pectin. Langmuir 2014;30(12):3441-3447. https://doi.org/10.1021/la500491c PMid: 24593694
Saravanakumar K, Sriram B, Sathiyaseelan A, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and cytotoxicity of starch-encapsulated biogenic silver nanoparticle and its improved anti-bacterial activity. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2021;182:1409-1418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.05.036 PMid: 33965484
Padil VVT, ?erník M. Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using gum karaya as a biotemplate and their antibacterial application. International Journal of Nanomedicine 2013;8(1):889-898. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S40599 PMid: 2346739752.
Raffi M, Mehrwan S, Bhatti et al. Investigations into the antibacterial behavior of copper nanoparticles against Escherichia coli. Annals of Microbiology 2010;60(1):75-80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-010-0015-6
Amer M, Awwad A. Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles by Citrus limon fruits extract, characterization and antibacterial activity. Chemistry International 2021;7(1):1-8.
Liang X, Sun M, Li L, et al. Preparation and antibacterial activities of polyaniline/Cu0.05Zn0.95O nanocomposites. Dalton Transactions 2012;41(9):2804-2811. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2DT11823H PMid: 22249414
Choudhury B, Leoff C, Saile E, et al. The structure of the major cell wall polysaccharide of Bacillus anthracis is species-specific. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2006;281(38):27932-27941. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M605768200 PMid: 16870610
Banerjee A, Somani VK, Chakraborty P, et al. Molecular and genomic characterization of PFAB2: A non-virulent Bacillus anthracis strain isolated from an Indian hot spring. Current Genomics 2019;20(7):491-507. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389202920666191203121610 PMid: 32655288

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) 2024 Electronic Journal of Biotechnology